Hypotheses
- H1. Grade point average (GPA) determines Intelligence Quotient (IQ) scores among ninth graders.
- H0. GPA does not determine IQ scored among ninth graders.
GPA as an average outcome of a student’s performance is an indicator of their intelligence or ability to understand taught concepts. This capacity is significantly related to a child’s IQ as it also measures their general intelligence. In this study, a sample of 30 ninth graders aged 14-year-olds undertakes the Wechsler Intelligence Scale test for comparison with their grade point average (GPA) scores.
Variables
The study variables include the GPA grades and IQ scores. GPA grades are the independent variable, and IQ scores as the dependent variable. Both the GPA scores and IQ ratings are measured using an ordinal scale of measurement due to no absolute zero.
GPA and IQ scores show a positive correlation with an average strength of co-relation. In other words, a higher GPA is linked to superior IQ scores among the ninth-graders, as shown in the figure below.
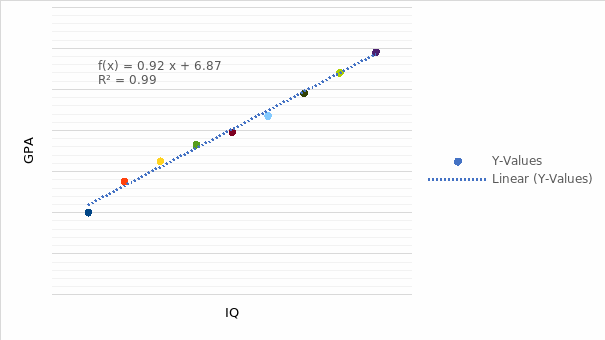
The relationship’s strength is moderate as it shows a perfect graph on a y-axis of y = 0.9183x + 6.8667 and R² = 0.9922. Higher GPA scores link to better IQ scores, implying that students who perform well in class have a higher IQ level than those whose GPA scores are lower. The findings reject the null hypothesis stating no existence of a relationship between GPA and IQ scored. Thus, there is a need to accept the alternative idea that GPA determines IQ scores as a higher GPA reflects superior IQ scores.
This analysis aimed to offer empirical research on the relationship between IQ and academic performance. Intelligence is among the best indicators of academic success for learners. Cognitive skill assessments predict academic achievement. School performance is used to validate IQ assessments. On the other hand, IQ assessments seldom account for most of the variation in academic achievement, implying that variables other than performance led to student disparities in test scores (Rakhmanov & Dane, 2020). General mental skills, also known as executive function skill and broad intellect, are a well-researched model with compelling reasons for critical forecasting results such as work success and career achievement. There is also some proof that general mental capacity predicts pupils’ academic success (Rakhmanov & Dane, 2020). A cumulative score is obtained from structured assessments or achievement tests designed to measure human intelligence or IQ. Children with high intellect test scores, for instance, outperform those with lower grades in education.
Intelligence is a person’s collective or aggregate capacity to behave deliberately, rationally, and cope efficiently with the world. General intellectual capacity (also known as intelligence quotient) is a term used to describe a person’s overall or general level of intellect (Akubuilo et al., 2020). The intelligence quotient (IQ) is important for voluntary involvement in core behaviors such as schooling, self-care, adulthood, work, and independent living. Global IQ metrics demonstrate a person’s overall “ability to grasp abstract concepts, respond successfully to the world, benefit through experience, participate in diverse ways of logic, and solve challenges through thinking. Environmental and biological influences both control intelligence. Intellectual ability and academic success are distinct but linked terms since intelligence is thought to be an effective cognitive variable influencing achievement rates.
One of the predictors of low school success in learners is intellectual ability (computed as IQ). Academic success affects potential wellbeing and is, therefore, a significant public health issue. With its corresponding chance of school dropout, poor school achievement contributes to potential wage decreases and thereby reinforces the cycle of poverty from one generation to another. There are also contradictory studies in the literature about the association between IQ and educational success. Food, literacy, socioeconomic factors, gender, ethnicity, school style, age, and family size may impact IQ and academic success. In this study, IQ was positively correlated with GPA.
References
Rakhmanov, O., & Dane, S. (2020). Correlations among IQ, visual memory assessed by ROCF test and GPA in university students. Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Science, 8(3), 1-5.
Akubuilo, U. C., Iloh, K. K., Onu, J. U., Ayuk, A. C., Ubesie, A. C., & Ikefuna, A. N. (2020). Academic performance and intelligence quotient of primary school children in Enugu. The Pan African Medical Journal, 36(129) Web.
