The acquisition of creative thinking skills is both the tool and the ultimate goal of any learning process. Educational theorists describe the processes that people typically use when learning and using their critical thinking. For example, Bloom’s digital technology proposes to divide the thought process into 6 types of information processing. Mind mapping, and fishbone diagrams are examples of visual mapping of thinking processes. Creative thinking can be used successfully to solve various problems or philosophical dilemmas. The Six Hats tool is an interesting way of processing information prior to making decisions. In this paper the six tools of critical thinking concept, the Six Hats problem-solving approach and mind-mapping technique will be presented.
Bloom’s Levels of Creative Thinking Interpreted as Tools
There are six levels in Bloom’s taxonomy, including memorizing, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating. The creation is at the top of Bloom’s pyramid, as it is the most complex and comprehensive mind function. In perspective, Bloom’s creative thinking aspects can be used in practical studying in the modern digital world. Memorizing can be interpreted as “recognize, enumerate, describe, identify, get, highlight, highlight, bookmark, create social networks, bookmark on social networks, bookmark favorites, search, and google search” (“The best critical thinking tools,” 2021, par. 5). Creative thinking and any thinking would be impossible without the information to operate with. Digital tools can make memorizing better structured and the knowledge stored – more accessible. Tools like YouTube, PowToon, EdTED, Clarisketch, Cling, Pinterest or Reddit, Evernote Web Clipper, Trello and Stache can be very helpful.
The second aspect of creative thinking is understanding, which means “interpretation, demonstration, generalization, inference, paraphrasing, classification, comparison, explanation, advanced search, logical search, blog logging, tweets, categorization and labeling, commenting, annotating, subscribing” (“The best critical thinking tools,” 2021, par. 7). In other words, understanding is the compression of large amounts of information into simple, interrelated concepts. Using information already understood in creative thinking is more natural than using raw data; therefore, understanding is an inevitable second step. Tools like mind maps (customizable through Mindmaple and MindNode) can be practical at this stage.
Applying information is an even faster way to work with raw data. Application in the digital world means “implement, execute, use, execute, launch, download, play, work, hack, download, share, edit, edit a wiki” (“The best critical thinking tools,” 2021, par. 9). During the application phase, students can experiment with information and possibly find new, not yet existing uses. Examples of digital tools that allow applying learned information are video blogs and tools for them, such as Weebly and Edublogs.
Analysis of information is directly creative processing of data, since during the analysis a person compares new information received and freshly formed concepts, possibly tested in practice, with those learned and tested earlier. In the digital world, analysis is “comparison, organization, deconstruction, attribution, structuring, structuring, integration, linking, reverse engineering, hacking, smart mapping, validation, calculation” (“The best critical thinking tools,” 2021, par. 11). Digital tools that can be used in this respect are Lucidchart and Creately, for data visualization and plotting, or OneNote, Toodledo, and Google Docs for tasks that involve structuring and sketching.
Then, the assessment of information allows the student to make sure that the facts with which he operates are true and reliable, since the creative result depends on the reliability of the information. Evaluation is “checking, hypothesizing, criticizing, experimenting, judging, testing, discovering, monitoring, commenting on blogs or vlogs, reviewing, publishing, moderating, collaborating, networking, thinking, alpha or beta testing” (“The best critical thinking tools,” 2021, par. 13). In this context, tools to directly check the validity of a statement or opinion, such as Snopes and FactCheck.org, are suitable. Evaluation of information is also needed to determine its importance from different points of view or the level of applicability in different areas. Assessment and analysis have similarities but differ in general, as analysis deals with details, and assessment provides a broader perspective.
Finally, after completing all the listed manipulations or steps, students usually come to the final step – the creation of information. The creation of new information may consist in the involvement of outside experts who contribute new knowledge, or the student himself may become an expert after a long process of memorizing, understanding, applying, analyzing, and evaluating. Creation is “design, engineering, planning, production, invention, development, manufacture, construction, programming, filming, animation, blogging, video blogging, mixing, remixing, wiki site, publishing, video casting, podcasting, directing, producing” (“The best critical thinking tools,” 2021, par. 15).
There is a wide variety of digital tools for creating content, such as digital portfolio creation using Google Sites, Evernote and VoiceThread. Wix, WordPress and Ghost allow creating brands, Jahshaka, WeVideo or Magisto – quality videos. Given the above, it is obvious that creating information is not limited to writing texts; it is a much broader field for action.
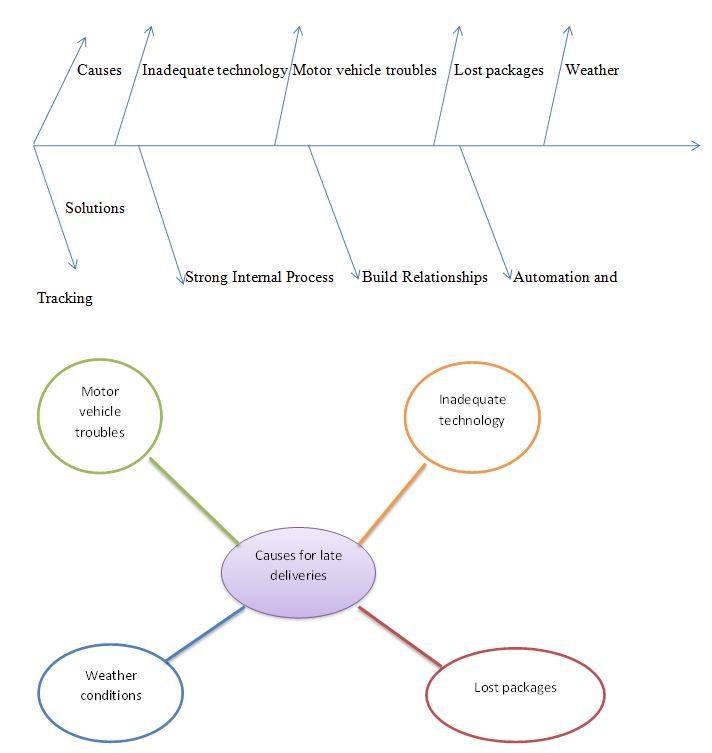
Mind Map and Fishbone Diagram for Late Delivery Problem
Late delivery can be a serious business concern given the need to meet the standards set by buyers and competitors. Therefore, businesses must understand the causes of this phenomenon and quickly find ways to solve emerging problems.
Applying “Six Hats” to the Problem
Six Thinking Hats is a technique invented by Edward de Bono, a researcher of creative thinking. In fact, these are six methods of structural thinking aimed at making decisions. The methods can be applied sequentially to solve different types of problems. They are an alternative to standard approaches such as discussion or debate. Each of the hats has its color and semantic content corresponding to the color (“The Six Thinking Hats,” 2021). Metaphorically, speaker puts on a hat, and chooses an approach to solving the problem. Applying only one hat at a time is possible by one person or group for the technique to work correctly. This method allows teams and individuals to think more broadly, creatively and thoroughly.
The Blue Hat is called Process and focuses on managing the thought process. This hat invites to reflect on the way of thinking, choose the right mindset, and plan actions. The White Hat is called Facts and focuses on known and needed information, facts and data. This hat assumes a neutral and objective approach, answering the questions of what we know, what we need to find out, and how we will get the information we need. Green Hat is called Creativity, where thinking focuses on creativity, this hat represents ideas, opportunities, alternatives, and solves problems of the Black Hat.
Red Hat is called Feelings and here thinking focuses on feelings, premonitions, and intuition. These are feelings right now that can change for reasons that need not be stated. The Yellow Hat is called Benefits, and it discovers the positives, pluses, values, and benefits by using logical arguments. Black Hat is called Cautions because it focuses on potential problems, difficulties and weaknesses, assesses why something is not working, and identifies risks and dangers, by making logical arguments.
Thus, the six tools of critical thinking concept, the Six Hats problem-solving approach and mind-mapping technique were presented. Six tools of creative thinking are memorizing, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating information. Mind mapping and fishbone diagrams are useful for understanding the new concepts. Finally, the Six Hats problem-solving approach allows to tap into all aspects of the creative mind to find the most thorough, creative, and broad perspective for solving a problem.
References
The best critical thinking tools aligned with Bloom’s taxonomy. (2021). Web.
The Six Thinking Hats. (2021). Web.
